DRYP Model
Overview
DRYP is a process-based distributed hydrological model developed to capture key hydrological processes across different climatic conditions. DRYP describes all relevant hydrological processes at surface and subsurface levels, including groundwater flow.
DRYP: Dryland Water Partitioning model
Model description and structure
The parsimonious water partitioning model is a process-based distributed hydrological model.
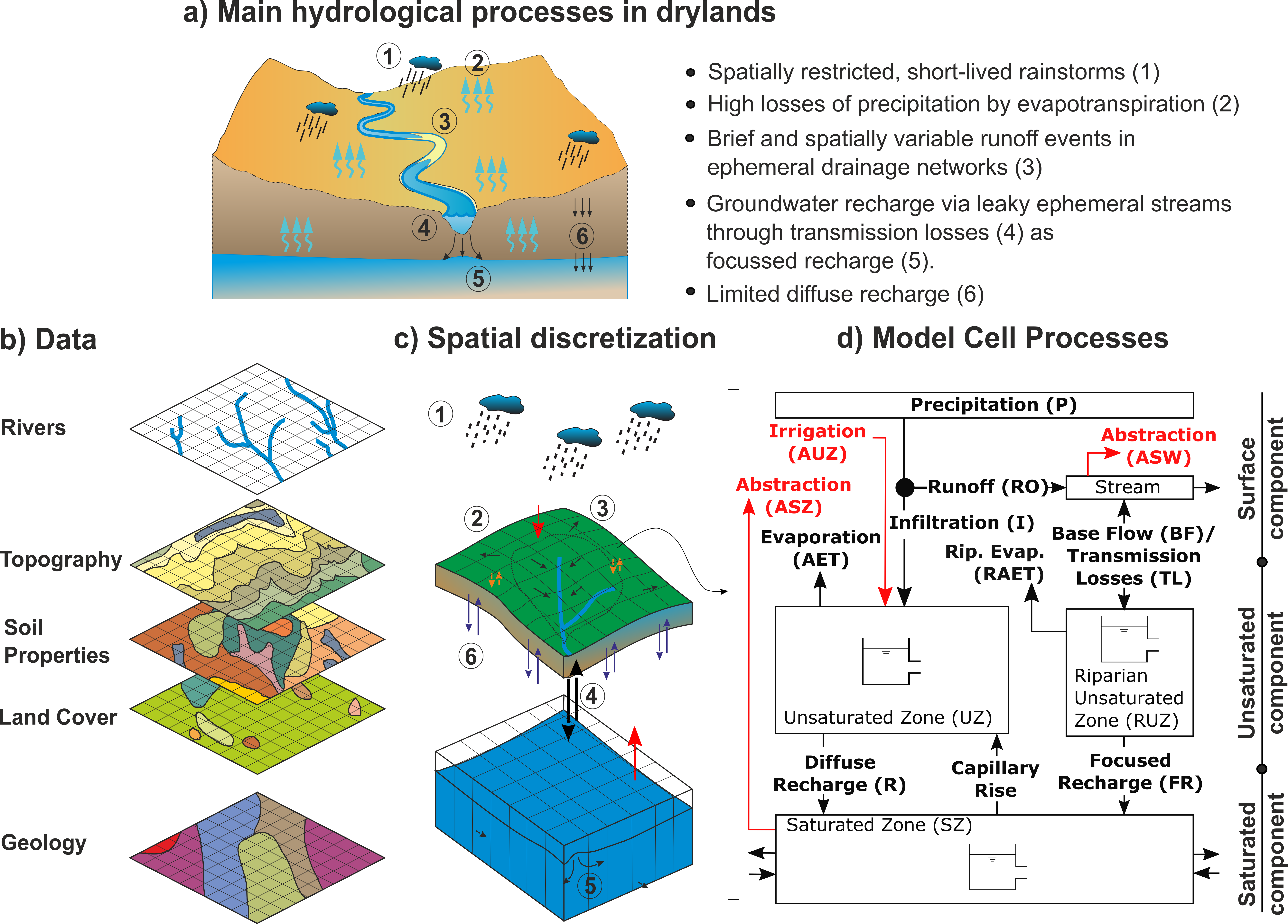
Model Hydrological Parameters
The model uses spatially distributed maps in raster format as input parameter files. If a parameter file is not provided, the model will use spatially uniform default values.
For the surface component:
- Digital elevation model (DEM): required (essential).
- River network length (in meters): values greater than zero are specified as rivers; if not available, all cells are considered rivers. Default value is the size of model grids.
- Flow direction in Landlab format: ID of receiving node following Landlab indexing. If not available, Landlab will automatically find the direction of flow based on the DEM.
- Model domain: a raster file indicating the basin. Default value is 1.0. If not provided, the entire grid will be assumed as the model domain.
- Channel width (in meters): default value is 10m.
In case of providing a flow direction file, it should follow Landlab conventions. A comprehensive description of Landlab flow direction conventions can be found here. Note that Landlab grids are labelled from 0 to n, where n is the number of cells (see here).
Below is an example of a flow direction raster format that follows Landlab conventions:
```plaintext ncols 5 nrows 4 xllcorner 574361 yllcorner 3502989 cellsize 1000 NODATA_value -9999 15 16 17 18 19 10 11 12 13 14 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4
Flow direction raster files must have values indicating the number of the next downstream cell. A cell value in the flow direction file matching the index indicates a sink point.
For the subsurface component the following parameters can be provided:
- Rooting depth in mm: default value 1000mm
- Path_uz_theta_wp: default value 0.1
- Total available water at wilting point (AWC): default value 0.10
- Porosity (n_e): default value 0.40
- Standard deviation of the saturated hydraulic conductivity, $\sigma$
- Infiltration at saturated conditions, ($K_{sat}$) in mm/h: default value 1.0 mm/h
- Water content at residual capacity, $\theta_r$
- Exponent of the water retention function (soil particle distribution), $b$: default value 10.5
- Suction head, $\psi$: default value 300mm
For the groundwater component:
- Factor_sz_kksat, $Ks_{GW}$: default value 1 [m/h]
- Aquifer specific yield, $Ks_{GW}$: default value 0.01 [-]
- Groundwater model domain: optional, in case the groundwater catchment differs from the surface catchment.
- Initial water table: default value specified at 1 meter below the rooting depth.
- Head boundary conditions: optional
- Flux boundary conditions: optional
- Streambed elevation: default value is 5m below the surface elevation.
Forcing datasets
DRYP requires time series as model forcing datasets. Precipitation and potential evapotranspiration must be provided in order to run the model; otherwise, it will throw an error. Datasets can be spatially variable (netCDF files) or uniform over the entire model domain (csv file).
Model outputs
Output variables for each model component are summarized below. The units of time depend on model settings, e.g., months.
Surface component:
- Runoff (
run), in mm/month - Infiltration rate (
inf), in mm/month - Transmission losses (
tls), m³/month - Streamflow (
dis), m³/month - Surface water storage, including rivers (
ssz), m³/month
Subsurface and riparian component:
- Soil (
tht) and riparian water content (thtrp), m³/m³ - Actual evapotranspiration from hillslope (
aet) and riparian area (etrp), mm/month - Groundwater diffuse (
dch) and focused (fch) recharge, mm/month - Groundwater recharge (
rch), mm/month
Groundwater component:
- Water table elevation (
wte), m - Groundwater discharge (
gdh), m³/month - Groundwater/Capillary evapotranspiration (
egw), mm/month - Total water storage deviation (
twsc), m/month
Water bodies:
- Total volume of water available - ponds (
vpd), m³ - evaporation - ponds (
epd), mm/month - Total abstractions - ponds (
apd), m³/month
Model parameters and setting files
Model input files are in JSON format, which can be created using a text editor like Notepad or a code editor like Visual Studio Code.
Input parameter file
All filenames’ parameters must be listed in the model parameters file, which is further explained below. However, if a parameter filename is not provided, default values will be used as model parameters.
Meteorological data required as forcing datasets must be provided. Information can be provided in netCDF format to account for spatial variability, or as a “.csv” file, which will assume a uniform rate over the entire model domain.
Filenames for forcing datasets should follow the format specified in the parameter setting file, and will depend on the number of files provided. If only one file is available, the file name can be written directly. However, for multiple files, the frequency will determine the format:
- Yearly files must specify the year as a number (e.g.,
IMERG-2000.nc). - Monthly files should have both the month and year specified (e.g.,
IMERG_2000-02.nc).
For the groundwater component, boundary conditions can be specified as head and flux boundary conditions. A raster file for head/flux must be provided if boundary conditions are considered in the model. The raster file will treat any value different from -9999 as a boundary condition.
To print results at specified locations, a file listing the x and y coordinates for each point must be provided. This file must contain at least one point located within the model domain; otherwise, an exception will occur. The format and specifications for output files are provided in the section on output files.
Coordinate files can be specified in the ‘OUTPUT’ section of the main configuration file.
Within the DRYP Settings file under “READING”-“data_reading” then “pre”/”pet, you can specify the type of METEO file you are using as such:
- 0 for csv files
- 1 for netCDF files
- 2 for YEARLY netCDF files
- 3 for MONTHLY netCDF files
- 4 for DAILY netCDF files
- 5 for ensamble netCDF files
It should be noted that if you are running the main cuwalid system (e.g. run_cuwalid() function), these settings will be changed automatically to match what is required from the output of Storm and stoPET.
Result files
Point result files are named with the model name followed by the letter “p” and the name of the variable at the end.
Model variable names and codes for point result files:
Surface component:
dis: Dischargetls: Transmission lossesinf: Infiltration excess
Unsaturated zone:
tht: Soil moistureaet: Actual evapotranspirationrch: Diffuse and focused recharge
Saturated zone:
wte: Water table elevation
Point result files are time series with the first column specified as “Date.” The number of columns in result files depends on the number of points specified in the coordinate files. Columns are labeled with the component and variable name, followed by an index (e.g., dis_0, dis_1, etc.).
DRYP automatically saves spatially averaged fluxes and water content of model compartments. The result file name has the suffix avg. Results are saved at time steps specified for the surface component.
Average results are saved in a comma-separated file that can be opened in Microsoft Excel or any text editor. The file contains the following information, with each variable’s code in the first line:
pre: Precipitationpet: Potential evapotranspirationrch: Rechargedis: Dischargeaet: Actual evapotranspirationtht: Soil water contenttwsc: Groundwater storageegw: Capillary evaporationbc: Flux at boundary conditiontls: Transmission losses